Name of the ingredient
Dihydrocapsiate
Definition of the ingredient
Dihydrocapsiate ((4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl) 8-methylnonanoate) belongs to a group of capsinoids first identified in the fruits of a non-pungent cultivar of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) and also occur naturally in chilli and sweet peppers. Synthetic dihydrocapsiate is produced via a method involving lipase-catalysed esterification of vanillyl alcohol and 8-methylnonanoic acid.
Structure:
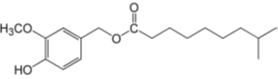
Molecular formula: C18H28O4
CAS Number: 205687-03-2
| Test | Method reference | Acceptance criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Description | ||
| Appearance | JSFA VII, General notices | Viscous, colourless to yellow liquid |
| Characteristics | ||
| Specific gravity | FCC V, Specific Gravity | 1.02 to 1.03 |
| Identification | ||
| Infrared spectroscopy | FCC V, Infrared Spectra | Transmittance at wave numbers 2953, 2928, 2855, 1733, 1519, 1278, 1241, 1036, 818, and 798 cm-1 |
| Assay | ||
| Dihydrocapsiate (DHC) | HPLC[1] | >p;94.0% |
| Test | Method reference | Acceptance criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Residual solvents | ||
| n-Hexane | GC-FID[2] | Not more than 5 mg/kg |
| Incidental metals and non-metals | ||
| Lead | FCC V, Lead Limit Test, Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric Method | Not more than 0.5 mg/kg |
| Magnesium | JSFA VII, Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry | Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Copper | JSFA VII, Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry | Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Arsenic | JP XIV, Arsenic Limit Test, Method 4 | Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium | FCC V, Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric Method | Not more than 0.5 mg/kg |
| Mercury | JSFA IX, Cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry | Not more than 1 mg/kg |
| Other organic or inorganic impurities or toxins | ||
| Side chain fatty acid | HPLC[3] | 2 to 7% |
| Related substances | HPLC[4] |
Vanillyl alcohol: Not more than 1.0% Total of Other Related Substances: Not more than 2.0% |
| Tetrahydrofuran | GC-FID[5] | Not more than 5 mg/kg |
Footnotes
| [1] | HPLC: Column: ODS-3 (4.0 mm x 100 mm, 3 µm); Mobile phase: 1.36 g/L potassium dihydrogenphosphate solution; Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; Column temperature: 40°C; Wavelength: 280 nm. |
|---|---|
| [2] | GC - FID: Detector: Hydrogen flame-ionisation detector; Column: GL Sciences, Inert Cap 1(0.25 mm I.D. × 60 m, 0.25 µm) df; Column temperature: 40°C (5 min) to 80°C at 10°C/min, to 320°C at 80°C/min, 320°C (15 min); Carrier gas: Helium; Flow rate: 26 cm/sec; Split ratio: 1:10 |
| [3] | HPLC: Column: YMC-Pack FA (6.0 mm x 250 mm, 5 µm); Mobile phase: 1 mL of acetonitrile, water, and trifluoroacetic acid (650:350:1) mixture to 1000 mL of acetonitrile and water (13:7) mixture; Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; Column temperature: 25°C; Wavelength: 390 nm. |
| [4] | HPLC: Column: ODS-SP (4.0 mm x 100 mm, 3 µm); Mobile phase A: 1.36 g/L potassium dihydrogenphosphate solution/acetonitrile (700:300), Mobile phase B: 1.36 g/L potassium dihydrogenphosphate solution/acetonitrile (200:800); Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; Column temperature: 40°C; Wavelength: 210 nm. |
| [5] | GC-FID: Detector: Flame ionisation detector; Column: Fused silica tube of inner diameter 0.53 mm and length 30 m with the inner surface coated with 6% cyanopropylphenyl-94% dimethylpolysiloxane for gas chromatography to a thickness of 3 μm2); Column temperature: Injected at a fixed temperature of around 40°C, to 80°C at 5°C/min, to 240°C at 80°C/min, 240°C (5 min); Carrier gas: Helium; Linear velocity: 35 cm/s; Split ratio: 1:5. |
Key to abbreviations
BP = British Pharmacopoeia
FCC V = Food Chemicals Codex, Fifth Edition
GC = Gas Chromatography
FID = Flame ionisation detector
HPLC = High-pressure liquid chromatography
IR = Infrared spectrophotometry
JSFA VII = The Japanese Specifications and Standards for Food Additive, Seventh Edition
JSFA IX = The Japanese Specifications and Standards for Food Additives, Ninth Edition
PCBs = Polychlorinated biphenyls
Ph Eur = European Pharmacopoeia
TLC = Thin layer chromatography
USP = United States Pharmacopoeia

