Name of the ingredient
Lacto-N-neotetraose (AAN)
Definition of the ingredient
Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) is a white to off-white crystalline powder or agglomerates that is produced either by chemical synthesis or by a microbiological process (with a genetically modified strain of Escherichia coli K12 DH1). LNnT is isolated by crystallisation.
Molecular formula: C26H45NO21
Structure:
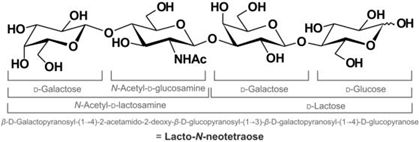
CAS Number: 13007-32-4
| Test | Method reference | Acceptance criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Description | ||
| Appearance | ISO 6658 | Powder, agglomerates, powder with agglomerates |
| Colour | ISO 6658 | White, white to off-white, off-white |
| Characteristics | ||
| pH in 5% solution (20°C) | Ph Eur 2.2.3 |
5.0 to 7.0 (for chemical synthesis) 4.0 to 7.0 ( for fermentation) |
| Water | Karl-Fischer (Ph Eur 2.5.12) | ≤9.0% w/w |
| Identification | ||
| NMR |
Strecker et al. 1989[1] Kuhn et al. 1956[2] |
Recorded NMR spectra must be in full agreement with the structure of LNnT. |
| MS |
Chai et al. 2001[3] Pfenninger et al. 2002[4] |
Base molecular ion peak matches molecular weight. |
| HPLC |
HPLC (for chemical synthesis)[5] HPLC (for fermentation)[6] |
Retention time of the main peak corresponds to retention time of LNnT standard ±3%. |
| HPAEC |
HPAEC (for chemical synthesis)[7] HPAEC (for fermentation)[8] |
Retention time of the main peak corresponds to retention time of LNnT standard ±3%. |
| Assay | ||
| Assay (water free) Lacto-N-neotetraose |
HPLC (for chemical synthesis)[5] HPLC (for fermentation)[6] |
≥96.0% w/w for chemical synthesis ≥92.0% w/w for fermentation |
| D-Lactose |
HPAEC (for chemical synthesis)[7] HPAEC (for fermentation)[8] |
≤1.0% w/w for chemical synthesis ≤3.0% w/w for fermentation |
| Lacto-N-triose II |
HPAEC (for chemical synthesis)[7] HPAEC (for fermentation)[8] |
≤0.3% w/w for chemical synthesis ≤3.0% w/w for fermentation |
| para-Lacto-N-neohexaose† | HPAEC[8] | ≤3.0% w/w |
| LNnT fructose isomer |
HPLC (for chemical synthesis)[5] HPLC (for fermentation)[6] |
≤0.6% w/w for chemical synthesis ≤1.0% w/w for fermentation |
| Total Human-identical milk saccharides (water free) assay‡ | Calculated theoritically as the summation of percentages of LNnT, D-lactose, lacto-N-triose II, and para-lacto-N-neohexaose. | ≥95.0% w/w |
| Notes: | ||
|
† Only for LNnT produced by fermentation. ‡ Human-identical milk saccharides is defined here as "the sum of LNnT, D-lactose, lacto N-triose II, para-lacto-N-neohexaose" and is considered only for the fermented product. |
||
Footnotes
| [1] | Strecker, G., Wieruszeski, J. M., & Montreuil, J. (1989). Assignment of the 1H-and 13C-NMR spectra of eight oligosaccharides of the lacto-N-tetraose and neotetraose series. Glycoconjugate journal, 6(1), 67-83. |
|---|---|
| [2] | Kuhn, R., & Baer, H. H. (1956). Die Konstitution der Lacto‐N‐tetraose. Chemische Berichte, 89(2), 504-511. |
| [3] | Chai, W., Piskarev, V., & Lawson, A. M. (2001). Negative-ion electrospray mass spectrometry of neutral underivatized oligosaccharides. Analytical chemistry, 73(3), 651-657. |
| [4] | Pfenninger, A., Karas, M., Finke, B., & Stahl, B. (2002). Structural analysis of underivatized neutral human milk oligosaccharides in the negative ion mode by nano-electrospray MS n (Part 1: Methodology). Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 13(11), 1331-1340. |
| [5] | HPLC: Column: TSKgel Amide-80 (150 mm x 4.6 mm, 3 µm); mobile phase: Acetonitrile/Water (Gradient); Flow rate: 0.9 mL/min; Column temperature 25° UV detector 208 nm. |
| [6] | HPLC: Column: apHera NH2 polymer (250 mm x 4.6 mm, 5 μm); mobile phase: Acetonitrile/Water (Gradient); Flow rate 1.1 mL/min; Column temperature 25°C; UV detector 205 nm. |
| [7] | HPAEC: Column: CarboPac PA1 (2 mm x 250 mm); mobile phase: 100 mM NaOH/20 mM NaOAc; Flow rate 0.25 mL/min; Column temperature 25°C. |
| [8] | HPAEC: Column: CarboPac PA200 (3 mm x 250 mm with 3 mm x 50 mm guard column); mobile phase: 500 mM NaOH/100 mM NaOH/water (Gradient); Flow rate 0.45 mL/min; Column temperature 25oC; Detector compartment temperature 35°C. |
| Test | Method reference | Acceptance criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Residual solvents | ||
| Methanol† | GC-HS (Ph Eur 2.4.24) | ≤100 mg/kg |
| Residual solvents (methanol, 2-propanol, methyl acetate, acetone)* | GC-HS (Ph Eur 2.4.24) |
≤50 mg/kg individually ≤200 mg/kg in combination |
| Incidental metals and non-metals | ||
| Lead | ICP-MS by EN 13805; EN 15763 or EPA 6020A | ≤0.1 mg/kg |
| Arsenic | ICP-MS by EN 13805 or EN 15763 | ≤0.1 mg/kg |
| Cadmium | ICP-MS by EN 13805 or EN 15763 | ≤0.1 mg/kg |
| Mercury | ICP-MS by EN 13805 or EN 15763 | ≤0.01 mg/kg |
| Palladium* | ICP-MS by EPA 6020A | ≤0.1 mg/kg |
| Nickel* | ICP-MS by EPA 6020A | ≤3.0 mg/kg |
| Other organic or inorganic impurities or toxins | ||
| Ash, sulphated | Ph Eur 2.4.14 | ≤0.4% w/w |
| Residual proteins | Bradford Assay (UV-001) | ≤0.01% w/w |
| Residual Endotoxins | Ph Eur 2.6.14 (LAL kinetic chromogenic assay) | ≤10 EU/mg |
| Acetic acid (as free acid and/or sodium acetate)* | EN ISO 10304-1 | ≤0.3% w/w |
| Notes: | ||
|
† Only for LNnT produced by fermentation. * Only for LNnT produced by chemical synthesis. |
||
Key to abbreviations
EPA = United States Environmental Protection Agency
EU = Endotoxin units
EN = European norms
GC = Gas chromatography
GC-HS = Gas chromatography - headspace
HMO = Human milk oligosaccharides
HPLC = High-pressure liquid chromatography
HPAEC = High perfomance anion exchange chromatography
ICP-MS = Inductively coupled plasma - mass spectrometry
ISO = International organisation for standardisation
LNnT = Lacto-N-neotetraose
MS = Mass spectrometry
NMR = Nuclear magnetic resonance
Ph Eur = European Pharmacopoeia

